Understanding Body Fat and Its Implications on Health
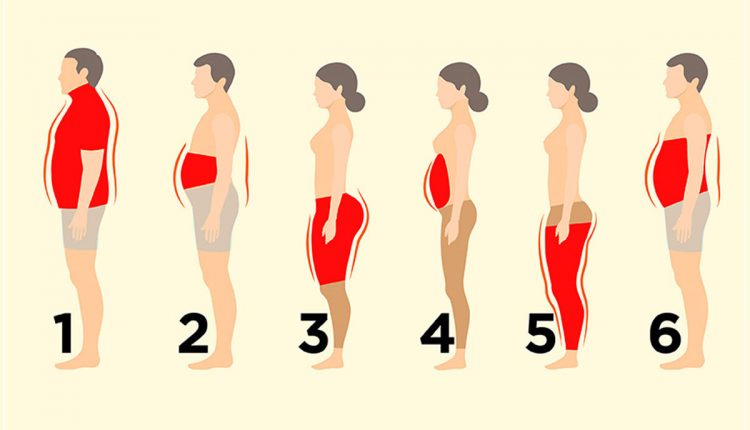
Understanding body fat and its implications on health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. The type, distribution, and amount of body fat can significantly influence your health. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of body fat, their health implications, and what you can do to manage them effectively.
Types of Body Fat
1. Subcutaneous Fat

Subcutaneous fat is the most visible type of fat, located directly under the skin. This is the fat you can pinch on your arms, thighs, and abdomen. While some subcutaneous fat is necessary for insulating the body and protecting muscles and bones from trauma, excessive amounts can lead to health problems.
Health Implications:
- Excessive subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of metabolic disorders.
- It is associated with higher levels of inflammation.
- Can lead to cardiovascular diseases if not managed properly.
Management Tips:
- Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle and reduce fat.
- Follow a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Stay active throughout the day with regular walking or other moderate activities.
2. Visceral Fat
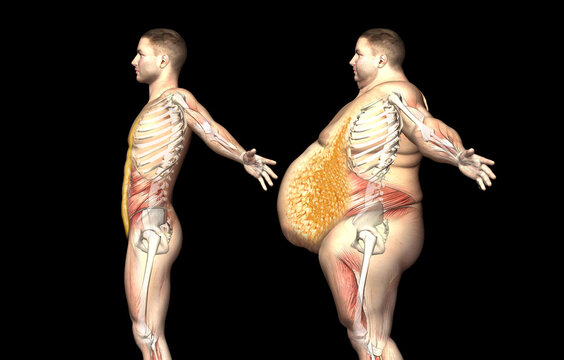
Visceral fat is the fat that surrounds your internal organs. It is not visible and can be much more harmful than subcutaneous fat. Visceral fat is metabolically active, meaning it can produce hormones and inflammatory substances that significantly impact your health.
Health Implications:
- Linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Associated with cardiovascular diseases.
- Can lead to insulin resistance and other metabolic syndromes.
Management Tips:
- Engage in high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to effectively burn visceral fat.
- Reduce the intake of refined sugars and processed foods.
- Increase fiber intake with whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
3. Brown Fat

Brown fat is a type of fat primarily found in infants but also present in small amounts in adults. Unlike other types of fat, brown fat burns calories to generate heat. It is considered beneficial and is the subject of much research.
Health Implications:
- Helps regulate body temperature.
- Can improve metabolism and aid in weight management.
- May protect against obesity and metabolic diseases.
Management Tips:
- Exposure to cold temperatures can activate brown fat.
- Certain foods like green tea and capsaicin (found in chili peppers) may help stimulate brown fat activity.
- Regular physical activity can promote the formation of brown fat.
4. White Fat

White fat is the most common type of fat in the body. It stores energy and insulates the organs. However, in excess, it can lead to various health issues.
Health Implications:
- Excessive white fat is linked to obesity.
- Increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Can contribute to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Management Tips:
- Monitor calorie intake to avoid excessive fat accumulation.
- Focus on a balanced diet with healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts.
- Consistent aerobic exercise helps in reducing white fat.
5. Beige Fat

Beige fat is a type of fat that is a mix between brown and white fat. It has the ability to burn calories and is activated by certain environmental factors like cold exposure.
Health Implications:
- Can help in burning excess calories.
- Aids in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Potentially reduces the risk of obesity-related diseases.
Management Tips:
- Engage in regular physical activities to stimulate beige fat.
- Practice thermogenesis through cold showers or spending time in cooler environments.
- Include foods and supplements that promote the browning of white fat cells.
Distribution of Body Fat
The distribution of body fat is as important as the type. Fat distribution can determine your risk for various health conditions. Two common patterns are:
Apple-shaped Body

People with an apple-shaped body tend to carry more weight around their abdomen. This type of fat distribution is associated with higher levels of visceral fat.
Health Risks:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Higher likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Greater risk of metabolic syndrome.
Management Tips:
- Focus on abdominal exercises to target belly fat.
- Limit intake of alcohol, which can contribute to abdominal fat.
- Increase protein intake to reduce cravings and promote satiety.
Pear-shaped Body
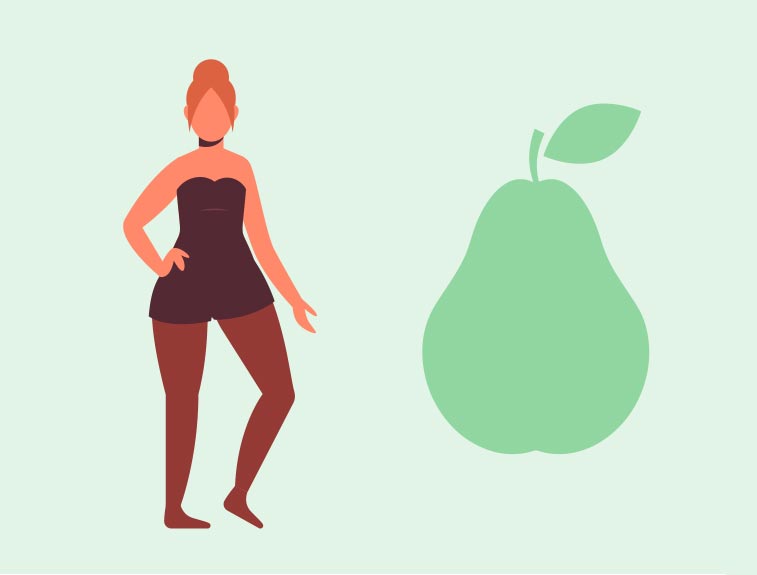

Individuals with a pear-shaped body carry more weight around their hips and thighs. This pattern is more common in women and is associated with higher levels of subcutaneous fat.
Health Risks:
- Lower risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to apple-shaped bodies.
- Reduced likelihood of metabolic syndrome.
- Potential risk of osteoarthritis due to increased weight on the lower body.
Management Tips:
- Incorporate lower body strength training exercises like squats and lunges.
- Maintain a balanced diet with adequate calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
- Engage in regular aerobic exercises to manage overall body fat.
Impact of Body Fat on Health
1. Cardiovascular Health
High levels of visceral fat are particularly harmful to cardiovascular health. This type of fat increases the risk of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart attacks. Maintaining a healthy body fat percentage through diet and exercise is crucial for preventing cardiovascular diseases.
Management Tips:
- Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engage in regular cardiovascular exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels regularly.
2. Metabolic Health
Body fat, especially visceral fat, plays a significant role in metabolic health. Excessive fat can lead to insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Monitoring and managing body fat through lifestyle changes can help maintain metabolic health.
Management Tips:
- Reduce the intake of sugary drinks and high-glycemic index foods.
- Include foods high in fiber, which can improve blood sugar control.
- Practice portion control and mindful eating to avoid overeating.
3. Hormonal Balance
Body fat influences hormonal balance. Excessive fat can lead to an overproduction of certain hormones, contributing to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women and low testosterone levels in men.
Management Tips:
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Avoid endocrine disruptors found in certain plastics and chemicals.
- Manage stress levels, as chronic stress can impact hormone production.
4. Inflammation
Adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, can produce inflammatory cytokines that contribute to chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Management Tips:
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, nuts, and leafy greens into your diet.
- Avoid processed foods and trans fats, which can increase inflammation.
- Engage in regular physical activity to reduce inflammatory markers.
Managing Body Fat for Better Health
1. Healthy Diet
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber is essential for managing body fat. Reducing the intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can help lower body fat levels.
Dietary Tips:
- Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits for vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains for better fiber intake.
- Include healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and seeds.
2. Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercises like running and anaerobic exercises like weight lifting, is vital for burning fat and maintaining a healthy body composition.
Exercise Tips:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week.
- Include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Incorporate flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga or Pilates.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to weight gain and an increase in visceral fat due to the overproduction of cortisol, a stress hormone. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress levels.
Stress Management Tips:
- Practice deep breathing exercises to reduce stress.
- Engage in activities you enjoy, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones.
- Ensure you have a support system to help manage stressors.
4. Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to weight gain. Ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and managing body fat.
Sleep Tips:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
- Create a restful sleep environment by keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
5. Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can aid in weight management. Drinking adequate water helps regulate metabolism and can prevent overeating.
Hydration Tips:
- Drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, more if you are physically active.
- Consume water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid sugary drinks and excessive caffeine.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of body fat and their health implications is essential for maintaining overall well-being. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, you can effectively manage body fat and reduce the risk of related health issues.
Taking proactive steps to understand and manage your body fat can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life. Whether it's making dietary adjustments, incorporating more physical activity, or simply managing stress better, each small change can make a significant difference. Remember, it's not just about the quantity of body fat but its type and distribution that can influence your health.
